CONSTANTINOPOLE BECOMES ISTANBUL
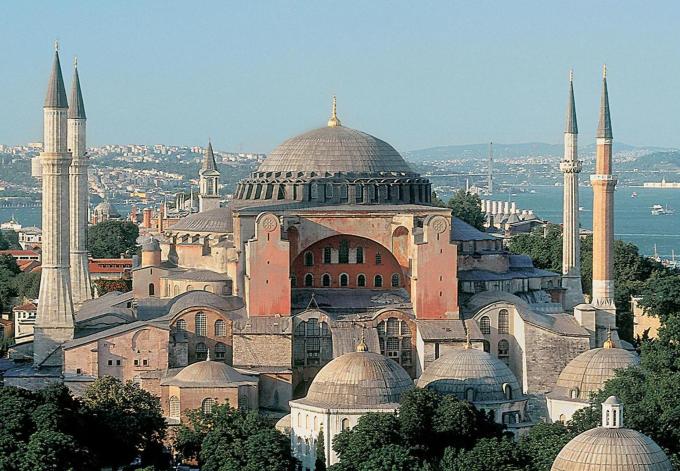
After the war Ottomans took the city of Constantinople and named it Istanbul, Sultan Mehmed allow non-Muslim nations to stay in peace and he order to build markets of Kapalı Carsı which had square capped with rounded. The Bedesten a fortified combined for luxury goods. In the two decades the population of Istanbul doubled and over the years it become the largest city of the world again. Art and science was important for the young sultan and he brought artist and scientists from Italy to Istanbul and the capital showed the influence of Italian engineering for example golden gate, star shaped fort of Yedikule, the round towers of Rumeli Hisarı. The young Sultan considered the majestic Hagia Sophia as his greatest prize and he quickly converted this huge church to a royal mosque with adding minarets. Apart from the changing in architecture, there was a political message he wanted to give this to European countries.
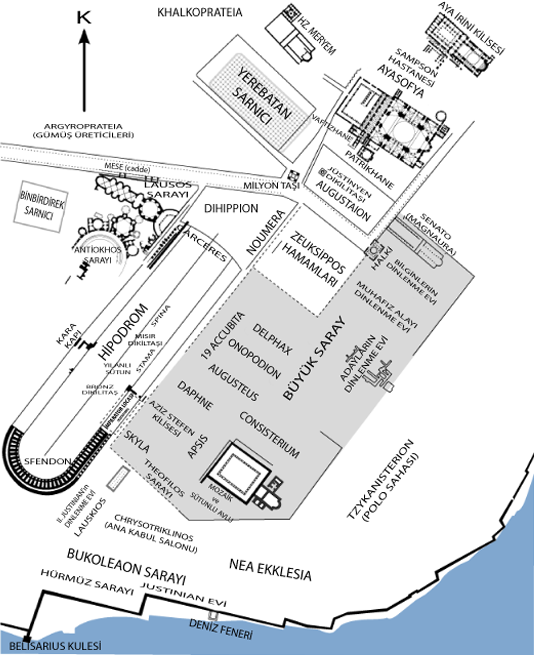 (Plan of Constantinopole)
(Plan of Constantinopole)
 (Illustration of Constantinopole)
(Illustration of Constantinopole)

Sultan Mehmed built the Fatih mosque in Bursa. It has a different type when we compare with others, It followed the hypostyle model found throughout south Asia. This mosque occupied the center of a extensive, perfect square plaza.
Sultan Mehmed decided to move his palace into the city where the acropolis of the ancient Greek city of Byzantium was stood. The design of Topkapı palace contained willfully asymmetry and more like a garden than a building it had a powerful relations between the nature and the framed views Bosporus landscapes made Topkapı more close to a Chinese Scholar’s garden than to the geometrically coordinated Italian Palazzo. Topkapı palace organized on a transition part of three courts which were integrated and elaborated throughout the 16th century. The imperial gate into the first stood a few steps from the apse of Hagia Sophia. There are numerous and various freestanding pavilions into the middle gate. Topkapi Palace which brings together the richest collection of Ottoman tiles and decorative arts, is truly a living museum. The most important part of the palace was the Diwan. Because the empire was managed in this council hall, stand out into the northwest courtyard of the arcade. Behind the Diwan lay the Harem, Harem was a collection of small and added courts also densely packed chamber on three levels, providing the residence for the Sultan’s female slaves. Relation to outside of Harem supplied by ‘ Araba Gate’, when they enter the gate from outside , they usually pass through the part of the slave’s master part which is also located in the Harem territory. Fatih’s Harem was substantially reconstructed in the 16th century during the long reign of Suleyman. During this period named as Reign of Women by historians because of the Hürrem and Mother Queen of Suleyman, Ottomans built an apartment in the northern corner of the Harem. The L shaped series of rooms was beautifully tiled, each room has a loftydome. 
(Topkapı Palace)
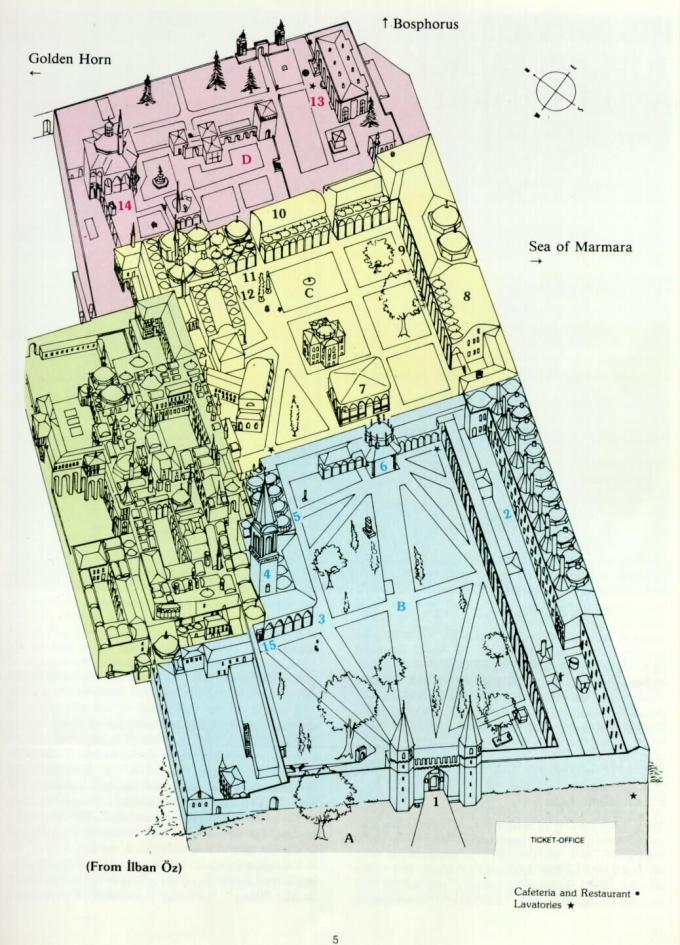
(Plan of the Topkapı Palace)
SINAN THE ARCHITECT
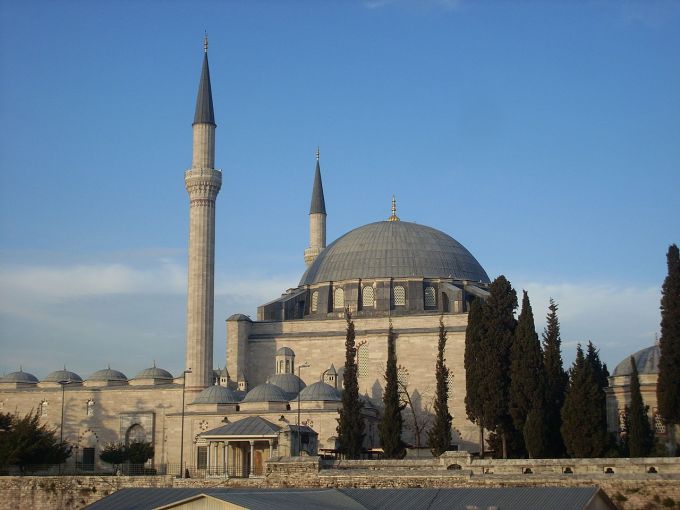
Sinan was the greatest architect of the Ottoman renaissance 1490-1588. Only in Istanbul he designed 22 major mosques and also imarets, He traveled a lot in this huge empire and he learned the solutions of engineering too so this knowledge allow him to design amazing bridges and transport ships too. Sinan started to work with Hürrem’s order ad he covered the mosque with a single hemispherical dome and designed a hospital with an unusual octagonal court, we can see amazing harmony in his construction all time like the Şehzade mosque. Sinan abutted the central dome with four semi domes and four buttress towers capped with vaults .Another important work of Sınan for the Ottoman architecture is that the earliest restoration of Hagia Sophia belongs to Mimar Sinan. This is the reasons why this great monumental mosque still survive till today.


(Haseki mosque )
PAPAL ROME
The ancient Rome architects inspire to Renaissance architects a system of symmetry, harmonious proportions, and decorative columns which they either copy to improve their architectural approach. The group that includes the famous artist Michelangelo presents their projects for churches, streets, palaces and villas promoted the city’s pilgrim trade while boosting the dynastic ambitions of papal families. The events that happen in religious rule in the Europe had two major results in architecture; first one is, it encouraged the development of new trials and regulations for fortification and urban design in reaction to the mobile cannon. The second thing is that, many of the designers who are under the pressure of the Papal Rome immigrated to other cities, taking with them the Roman language of classic architecture.
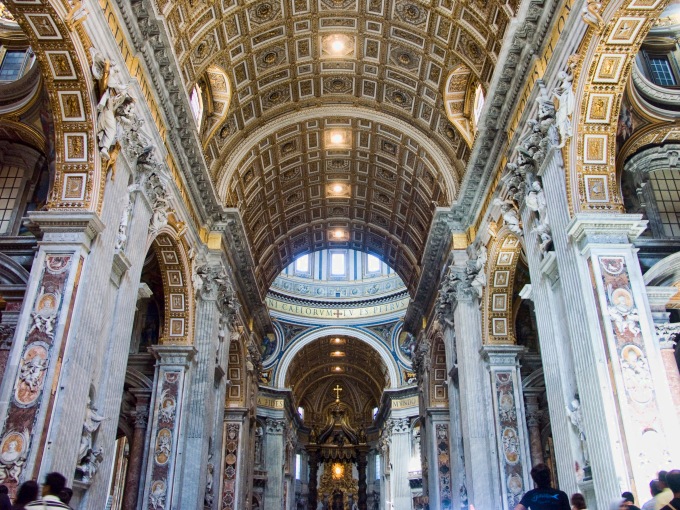
The ideologues of the Papal regime introduced theatrical papal ceremonials, luxurious costumes and new architectural settings or reconstruction of them, maybe the greatest example of this article is Pope Nicholas V who initiated the greatest project, demolition and rebuilding of old St. Peters rather than restore the basilica, Pope ordered the architect Bernardo Rossellino to demolish and rebuild the apse.

The Project of new palace Via Alessandrina started in 1501 and it served as the site for a few of the most sophisticated classical palaces in Rome. It appeared urbane because it has placed close to the Florentine ideal of civic beauty; this palace offered the model of urban scale for the new streets too.
 Ferdinand and Isabella commissioned to build a small domed shrine in Montoria in 1502. This reconstruction resembled an ancient round tholos-type temple. The carrying system set up with 16 columns these systems, sculpted metapes and tall drums revealed a new taste of plasticity
Ferdinand and Isabella commissioned to build a small domed shrine in Montoria in 1502. This reconstruction resembled an ancient round tholos-type temple. The carrying system set up with 16 columns these systems, sculpted metapes and tall drums revealed a new taste of plasticity